|
|
|
بازدید : 2323
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|
Because of my previous post, I discovered a book called ‘The Art of Strategy’ by Dixit and Nalebuff. I had read their first book called ‘Thinking Strategically’ published in 1993. Its focus is game theory applications in business discussing bargaining, unconditional moves, and vicious circles. It is fairly focused on dealing with opponents, which was – like Sun Tzu – quite popular at the time. When I wrote my first Novel ‘Deity’ in 2003, game theory was an intriguing subject that played a big part for a quantum computer who could not only predict, but influence the future. Game theory uses mathematical models to analyze decision-making for strategy, in which one individual’s decisions are based on the assumptions what the actions of other actors might be. When each player has adopted a strategy to play, an equilibrium can be reached. But that was only the beginning.
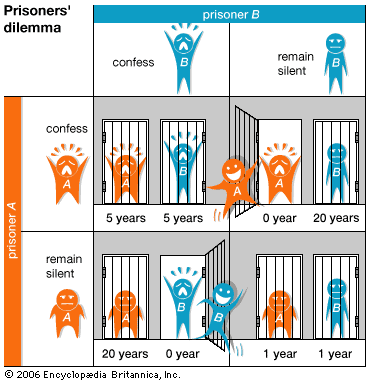
The Beginning: 'The Prisoners Dilemma Game'
The great minds of game theory are John von Neumann, Oskar Morgenstern and clearly John Nash for non-cooperative games. Most game theories are based on the idea of utility, meaning a rational, measurable benefit that one player can gain by acting a certain way. Game theory assumes that humans actors use similar abstract concepts in the sense of epistomology (what can be known) for their decision-making and for deciding upon actions. Not only the knowledge of the players is different, but most likely also their concepts of knowledge can be quite different. Our rationality needs however a model of reality to understand the means to act in a desired manner. It is in fact impossible for the decision-maker to know the complete state space and consequently all the possible actions by other players are not reasonably predictable as possibilities. It is therefore not surprising that behavorial economics discovered that most human decision-making is not based on rational utility. Some does even seem rather irrational, when it really isn’t, but uses heuristics such as bounded rationality (Gigerenzer et.al.) to decide under uncertainty. Evolutionary game theory assumes therefore no rationality or bounded rationality for its players and considers both biological and cultural evolution as well as individual learning.
Game Theory is thus still in development and only in 2007 Myerson, Hurwicz, and Maskin were awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics for their work in reverse game theory or mechanism design. They worked on game types where the rules of a game are actually designed while it is being played, with the designer having an interest to influence it’s outcome. Those concepts deal much more realistically with the real world of human-made rules and laws. It does have a strong similarity to the concepts of Adaptive Processes. One of the key elements is the necessity to extract information from the players that they would rather not divulge. The need to gather dependable decision-making information from uncooperative agents is a real business management problem.
I find these theories truly interesting in terms of mathematics, but with little practical application, mostly because of the mentioned epistomological modeling problem. All theoretical results are built on well-defined and controlled models that do not translate to the real world. The findings indicate however that the human mind can be dreadfully misled by thinking that these model concepts are real. In for example contract theory, a decision maker applies an optimization algorithm to achieve a ‘complete’ contract. He attempts to motivate players to take desired actions as maximizers of von Neumann-Morgenstern utility functions. Expected utility decision-making ASSUMES however the probability of various outcomes, thus the expected value of decisions is extremely sensitive to the assumptions, particularly with rare extreme events, a.k.a. as Black Swans. Enter the recent financial crisis!
Applying game theory for business strategy or management thus faces many obstacles, because doing business is in most cases not like a sequential or simultaneous game but an unknown mix of both with an unknown set of players under substantial uncertainty. Each real-world actor has a long tree list of dependent decisions to take that ought to be looked forward and reasoned backward in theory. Because the knowledge and possible actions of other players are mostly based on pure assumptions, it is a good strategy to retain the ability to change course en-route or allow for the renegotiation of agreements. Only in a few cases is reducing your options beneficial as an undoubtable signal, such as Cortés did in 1519 by scuttling his ships at Veracruz. He was intent to make his signals believable, because he also massacred thousands of the Aztec nobility to convince emperor Montezuma to capitulate.
What can we then learn for business from the study of game theory?
To burn your bridges or threaten your employees? I guess not. Yes, it is important that executives and managers send clear signals that are trustworthy. There is no difference, as asserted repeatedly by Dixit and Nalebuff, between employee and children behavior. “Either do this or else …” has to be followed by actions that assert the consequences. I see however the aspects of information exchange and information congruency for decision-making as the most important elements. The problem of ‘what we can know’ must be taken care of in business by creating a common information model for all players inside the business. Not a data model for programmers, but an information model for business people. Finally, empowerment ought to be used to motivate all players to act transparently and fill the model with realistic data. The “… or else …” is what I call boundary rules as an essential element of empowerment.
Bain & Company found in studies that 70% of all reorganizations do not improve anything and some actually worsen the state of the business. Next to a lack of accurate information, the core reason is that decision-making is not aligned with authority given. As only a few substantial changes can be executed at one time, change should not happen in Big-Bangs but continuously from the bottom-up by empowered employees. Also Forrester Research recently published a book focused on the subject, aptly named “Empowered.”
‘The Art of Strategy’ left me however dissatisfied, I guess because it retraces much of the original book with different examples and stories about threats, challenges and promises. While the book deals with strategically anticipating your opponent’s moves, it employs simple, counterintuitive common sense. Concepts like ‘put yourself in the opponents shoes’ and ‘actions speak louder than words’ are commonly accepted perspectives that I would not consider a scientific sensation. Also ‘countersignaling’ is not a new idea, explaining that those who belong don’t need to signal (=brag), while someone who i.e. lacks scientific credentials enforces the use of his PhD title. I have often said that the most prominent feature in ads is most likely the weakest aspect of a product. But competing by louder and more ads isn’t always the best approach. When cigarette TV advertizing was banned, tobacco companies fought it as they thought it would hurt them, but in fact because all companies suddenly did not have to compete through TV ads it substantially raised tobacco profits.
In conclusion it seems that most successful strategies are random chance and not achieved by applying a ‘complex systems thinking’ approach that tries to model all the complex dependencies of actions and reactions of all players in advance. Gut feelings and ‘guts to act’ are clearly more important than strategic models of business games, according to Gigerenzer. What remains for a business to improve is the need for real-time transparency to improve decision-making and for empowerment to translate the decisions into action. The business hierarchy is not about command and control but about proper role play in the business game. The executive needs to set strategic objectives, that are translated into targets by management, linked to goals by process owners, and executed as tasks by people skills to fulfill the customer outcome. Yes, doing business can be seen as a game, but it won’t be improved by theories and methodologies, but by empowering people with information technology and the means to fulfill the goals.
While a fool with a tool remains a fool, trying to execute a great strategy without the best in tools is plain dumb. A fool that needs a methodology to manage is outright dangerous. A wise general will create a strategy based on weapons technology available on both sides, because not to do so is gross negligence or even murder.
What can we take away from all this? Well, the concepts of information exchange in Game Theory support the importance of IT for running a business. The executive who designs a business strategy without understanding what information technology can provide and how the competition uses it, is endangering the future of his business.
Therefore, strategy has to follow real-world technology and not some theory.
:: برچسبها:
?Can Game Theory Improve Business Strategy ,
بازدید : 2498
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|
World Science News in Review
MIT Undergraduate Research Journal 19, 12 (Spring 2010)
Bacterial Behavior Sheds Light on Game Theory
Credit: Eshel Ben Jacob, ScienceDaily
Bacillus subtilis colonies.
The study of game theory, the science of how and why individuals make certain choices during competitive situations, has recently taken an interesting turn. Researchers have begun investigating the behavior of single-celled organisms in the hope of applying any newfound knowledge to human interactions.
Scientists at the University of California, San Diego’s Center for Theoretical Biological Physics have been using theoretical mathematics, chemistry, and physics to model the genomic and proteomic interactions among colonies of Bacillus subtilis under conditions of environmental stress.
Under stress, a bacterium faces two options. It can undergo sporulation, a process that involves more than 500 genes, in which the bacterium places a copy of its genome in a durable capsule known as a spore. These spores, which are extremely durable even during harsh conditions, can then germinate into new bacteria. The mother cell that sacrifices its genome to form the spore then bursts open releasing its intracellular contents to the environment.
The other option for the bacterium is to enter the “competence intermediate state” in which it makes its membrane more permeable to its extracellular environment so that it can assimilate the cellular contents released by other bacteria that have sporulated. Though this option may allow for survival, the bacterium risks death.
UCSD physics professor José Onuchic explains how these two options present a Prisoner Dilemma-like predicament: “It pays for the individual cell to take the risk and escape into competence only if it notices that the majority of the cells decide to sporulate. […] But if this is the case, it should not take this chance because most of the other cells might reach the same conclusion and escape from sporulation.”
The conclusion of the “game” is that only ten percent of the bacteria enter the “competence intermediate state.” The scientists have found that the decision a bacterium makes is dependent upon the chemical signals being released by its neighboring bacteria. Moreover, though the researchers keep refining their studies, they conclude that stochastic processes still pervade the decisions the bacteria make. Onuchic explains: “Another interesting fact is that the same cells in the same environment, in this case, bacteria in the colony, can actually in a statistical matter choose two different outcomes: sporulation or competence.”
The researchers hope their studies will have applications in sociology, economics, and even cancer biology.
http://murj.mit.edu/article.php?type=5&id=16
:: موضوعات مرتبط:
آﻣﻮزش و ﺗﺤﻘﯿﻘﺎت ,
,
:: برچسبها:
بیولوژی ,
بازدید : 2924
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|
http://www.gamesec-conf.org/papers.php
Game Sec 2010
Conference on Decision and Game Theory for Security
November 2010, Berlin, Germany
Mathias Humbert, Mohammad Hossein Manshaei, Julien Freudiger and Jean-Pierre Hubaux . "Tracking Games in Mobile Networks"
Robbert Fokkink, Steve Alpern, Joram Op den Kelder and Tom Lidbetter. "Disperse or Unite? A mathematical model of coordinated attack."
Soren Preibusch and Joseph Bonneau. "The Password Game: negative externalities from weak password practices"
Rainer Bohme and Mark Felegyhazi. "Optimal Information Security Investment with Penetration Testing"
Nan Zhang, Wei Yu, Xinwen Fu and Sajal Das . "gPath: A Game-Theoretic Path Selection Algorithm to Protect Tor's Anonymity"
Saurabh Amin, Galina A. Schwartz and Shankar S. Sastry. "Security Interdependencies for Networked Control Systems with Identical Agents"
Eitan Altman , Alireza Aram, Tamer Basar , Corinne Touati and Saswati Sarkar. "Robust Control in Sparse Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks"
List of Accepted Short Papers
Farzad Salim, Jason Reid, Uwe Dulleck and Ed Dawson . "Towards a Game Theoretic Authorisation Model"
:: برچسبها:
Game Sec 2010 ,
بازدید : 2358
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|
بازدید : 2217
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|
What Game Theory Can Tell Us About a Possible Armenian-Azerbaijani Conflict.
The four-year-old International School of Economics at Tbilisi State University (ISET) in Tbilisi, Georgia was founded to unite students and faculty from all three South Caucasus countries for a Western-style education in economics. And, as if undergoing a rite of passage in its growth as an institution, it underwent its first major academic controversy this year.
Students were agitated, donors threatened to withdraw funding and an ambassador warned of unilateral sanctions.
What caused all the fuss? — A master’s thesis that used game theory to create a model for the probability of war between Armenia and Azerbaijan.
Ani Harutyunyan, 23, originally of Vanadzor, Armenia, set out last November to create a model that could determine the probability of all-out war breaking out between the two countries over the disputed territory of Nagorno-Karabakh based on a variety of factors.
Now, mind you, creating a game theory model is not the same as predicting whether war will happen or not – it’s not a magic eight ball.
Basically it works like this: say you are hungry and the two main factors governing your action are price of the food and deliciousness of the food. You have three options to choose from:
1.) Don’t eat. You save your money, but you don’t resolve the problem.
2.) Throw something together at home. You expend very little money, but, although your bachelor-pad-borne concoction is filling, it’s hardly gourmet.
3.) Go out to eat. You’ll have to pony up some dough, but you’ll get some good food out of it.
And so, if you make a formula out of those choices and input subjective number values for your culinary pickiness and current level of poverty, one can compute which action you are most likely to take.
:: برچسبها:
Politics and game tneory ,
بازدید : 2339
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|
A Course in Game Theory
Publisher: The MIT Press | ISBN: 0262150417 | edition 1994 | PDF | 195 pages | 16,3 mb
A Course in Game Theory presents the main ideas of game theory at a level suitable for graduate students and advanced undergraduates, emphasizing the theory’s foundations and interpretations of its basic concepts. The authors provide precise definitions and full proofs of results, sacrificing generalities and limiting the scope of the material in order to do so. The text is organized in four parts: strategic games, extensive games with perfect information, extensive games with imperfect information, and coalitional games. It includes over 100 exercises.
:: برچسبها:
A Course in Game Theory ,
بازدید : 2462
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|
Apress.LINQ.for.VB.2005.Feb.2007.eBook-BBL
TITLE : LINQ for VB 2005 (Hardcover)
AUTHOR : by Fabio Claudio Ferracchiati (Author)
PUBLISHER : Apress publisher
ISBN : 1590598407
EDITION : 1st
PUB DATE : February 12, 2007
LANGUAGE : English
FORMAT : PDF
SIZE : 03 x 1.44 MB

Download :
http://www.megaupload.com/?d=D25CNTGD
:: موضوعات مرتبط:
ﮐﺎﻣﭙﯿﻮﺗﺮ و اﯾﻨﺘﺮﻧﺖ ,
,
:: برچسبها:
Apress - LINQ for VB 2005 ,
بازدید : 2471
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|
AppDev LINQ Using Visual C Sharp 2008 DVD | 1.33 GB
In this course, you’ll learn to use the exciting new .NET Framework 3.5 feature, Language Integrated Query (LINQ) to easily create complex data-independent queries. In addition, you’ll learn about the new language features added to Visual Basic in Visual Studio 2008 in order to make LINQ possible. You’ll start by working through a quick overview of LINQ, and how it applies to working with collections of objects, retrieving data stored in SQL Server, and creating XML content. Subsequent topics introduce new LINQ-oriented language features, LINQ to Objects, LINQ to DataSets, LINQ to SQL, LINQ to XML, and LINQ to Entities. By the time you’ve completed the course, you’ll have a good understanding of now only how to construct LINQ queries to work with data, but also how to use the features added to Visual Basic that support LINQ.
In this course, you will learn how to…
* Create new XML content using LINQ to XML.
* Iterate through collections of objects, using a single LINQ query.
* Use anonymous types, lambda expressions, extension methods, object initializers, and implicit type declaration.
* Query arrays, lists, dictionaries, and more using LINQ to Objects.
* Use the extension methods provided by the System.Linq.Enumerable class to extend the behavior of collection classes.
* Create an object model based on a SQL Server database and then query the database using LINQ to SQL.
* Modify data and use stored procedures with LINQ to SQL.
* Create XML content using classes in the System.Xml.Linq namespace.
* Validate, query and transform XML content using LINQ to XML.
* Transform XML content using LINQ to XML.
* Create an Entity Data Model based on a data source and then query the data using LINQ to Entities.
* Modify data and use stored procedures with LINQ to Entities.
Prerequisites: This course assumes that students have familiarity with .NET in general, and with specifically with programming ADO.NET. The course makes no attempt to explain basic Visual Studio 2008 or .NET Framework concepts, and assumes that the student is at least familiar with all the concepts covered in the Introduction to Programming and Developing Applications with Visual Studio 2008 courses.
http://hotfile.com/dl/14162365/a02f2f4/AppDev_LINQ_Using_Visual_C_Sharp_2008_DVD_www.newestwarez.com.part01.rar.html
http://hotfile.com/dl/14162522/699641c/AppDev_LINQ_Using_Visual_C_Sharp_2008_DVD_www.newestwarez.com.part02.rar.html
http://hotfile.com/dl/14162524/5034e3a/AppDev_LINQ_Using_Visual_C_Sharp_2008_DVD_www.newestwarez.com.part03.rar.html
http://hotfile.com/dl/14162379/2d1abc1/AppDev_LINQ_Using_Visual_C_Sharp_2008_DVD_www.newestwarez.com.part04.rar.html
http://hotfile.com/dl/14162531/13c76b2/AppDev_LINQ_Using_Visual_C_Sharp_2008_DVD_www.newestwarez.com.part05.rar.html
http://hotfile.com/dl/14162515/5d87d6f/AppDev_LINQ_Using_Visual_C_Sharp_2008_DVD_www.newestwarez.com.part06.rar.html
http://hotfile.com/dl/14162495/e6667ad/AppDev_LINQ_Using_Visual_C_Sharp_2008_DVD_www.newestwarez.com.part07.rar.html
:: برچسبها:
AppDev LINQ Using Visual C Sharp 2008 DVD ,
بازدید : 2454
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|

Packt Publishing | ISBN: 1847192548 | PDF | 252 pages | 6.56 MB
Introduction
When we say Language Integrated Query, we might think that it is already integrated into the programming language, just as we write SQL queries in our application. So what is the difference or additional features that we are going to get in LINQ? How is LINQ going to make our programming life easier? Also, I am sure that we all want to know how the new feature, LINQ, is making use of the other new features of C# 3.0. We'll see many of those in this book.
LINQ Architecture
Language Integrated Query is a new feature in Visual Studio 2008 that extends the query capabilities, using C# and Visual Basic. Visual Studio 2008 comes with LINQ provider assemblies that enable the use of Language Integrated Queries with different data sources such as in-memory collections, SQL relational database,
ADO.NET Datasets, XML documents and other data sources.
In Visual Studio 2008, Visual C# and Visual Basic are the languages that implement the LINQ language extensions. The LINQ language extensions use the new Standard Query Operators API, which is the query language for any collection that implements IEnumerable. It means that all collections and arrays can be queried using LINQ. The collections classes simply needs to implement IEnumerable, to enable it for LINQ to query the collections.
http://freakshare.net/files/ymtwybef/linq-quickly.pdf.html
:: برچسبها:
Linq Quickly ,
بازدید : 2414
نویسنده : TAKPAR
|
|

Product Description
Professional ADO.NET 3.5 with LINQ and the Entity Framework
LINQ and the Entity Framework are revolutionizing .NET database programming. With this book as your guide, you’ll discover how to leverage these cutting-edge query and object/relational mapping technologies for enterprise-class computing. It provides you with hands-on coding techniques for data-intensive web and Windows projects. You’ll also get quickly up to speed on LINQ technologies with the help of C# and VB programming examples.
Leading Microsoft database authority Roger Jennings first covers LINQ Standard Query Operators (SQOs) and domain-specific LINQ to SQL, LINQ to DataSet, and LINQ to XML implementations for querying generic collections. He then delves into the ADO.NET Entity Framework, Entity Data Model, Entity SQL (eSQL), and LINQ to Entities. Numerous code examples are integrated throughout the chapters that emulate real-world data sources and show you how to develop C# and VB web site/application or Windows projects.
The information in this book will give you the tools to create and maintain applications that are independent of the underlying relational data.
What you will learn from this book
* A new approach to data access in ADO.NET 3.5 SP1
* Methods for working with advanced LINQ query operators and expressions
* Techniques for querying SQL Server® database with LINQ to SQL
* Approaches for integrating third-party and emerging LINQ implementations
* How to raise the level of data abstraction with the Entity Data Model
* Steps for creating design-time data sources from ObjectContext
* Ways to use the Entity Data Model as a data source
Who this book is for
This book is for intermediate to advanced developers of data-intensive .NET web- and Windows-based applications.
Wrox Professional guides are planned and written by working programmers to meet the real-world needs of programmers, developers, and IT professionals. Focused and relevant, they address the issues technology professionals face every day. They provide examples, practical solutions, and expert education in new technologies, all designed to help programmers do a better job.
Product Details
* Paperback: 672 pages
* Publisher: Wrox (February 3, 2009)
* Language: English
* ISBN-10: 047018261X
* ISBN-13: 978-0470182611
http://hotfile.com/dl/31762718/52690a3/Wrox.Professional.ADO.NET.3.5.with.LINQ.and.the.Entity.Framework
:: برچسبها:
Professional ADO ,
NET 3 ,
5 with LINQ and the Entity Framework ,
|
|
|
